Why is effective communication more crucial than ever in today’s fast-paced business environment? SIP trunking has emerged as a transformative technology, revolutionizing how businesses manage their phone systems. How can understanding SIP trunking provide businesses with a competitive edge? By enhancing communication efficiency and reducing costs, SIP trunking offers significant advantages.
Did you know that over 60% of businesses have adopted SIP trunking, according to a recent survey? This statistic underscores its growing importance in the business world. This blog will explore what SIP trunking is, how it works, its benefits, and how businesses can transition to this innovative technology.
Read More: 6 Top IVR Routing Strategies to Improve Customer Journeys
What Is SIP Trunking?
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) trunking is a method used to deliver voice and other unified communications services over the internet. Unlike traditional phone lines that rely on physical connections, SIP trunking uses the internet to connect a company’s phone system to the public switched telephone network (PSTN). The term “trunking” refers to the grouping of multiple channels or lines, which enables efficient and scalable communication.
Trunking stands out from traditional phone lines due to its digital nature. Traditional phone lines are limited by physical infrastructure, whereas SIP trunks offer flexibility and scalability by leveraging internet connectivity. This distinction allows businesses to manage their communications more efficiently and cost-effectively.
How Does SIP Trunking Work?
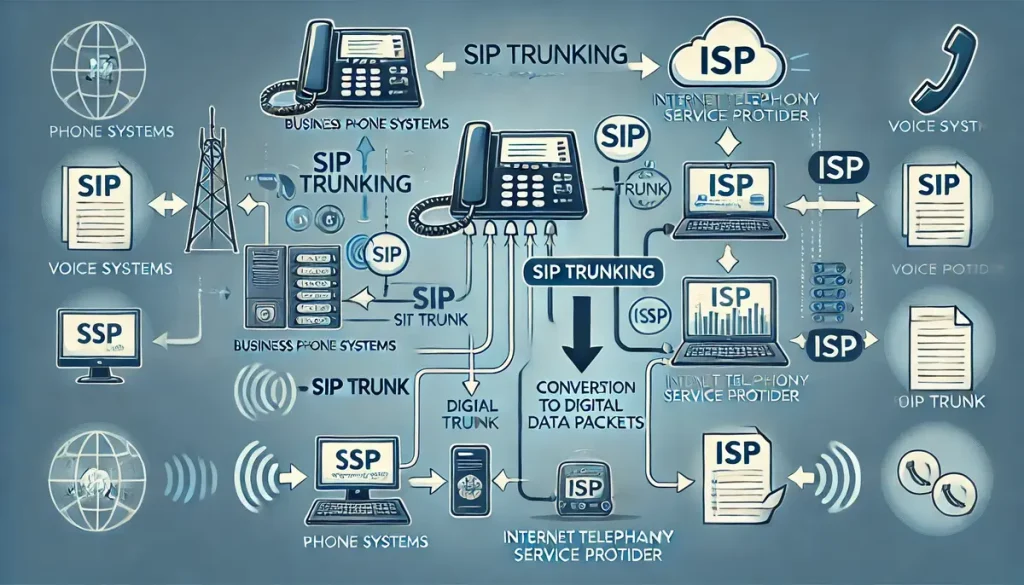
SIP trunking revolutionizes business communication by converting voice calls into digital data packets that travel over the internet. This modern approach eliminates the need for traditional phone lines, offering greater flexibility and efficiency. Let’s explore the detailed workings of SIP trunking.
Connection to ITSP
The first step in SIP trunking involves connecting your business phone system to an Internet Telephony Service Provider (ITSP). Here’s how it works:
- Establishing the Connection: Your business’s PBX (Private Branch Exchange) system connects to the ITSP over the internet. This connection allows for the routing of voice calls through the ITSP’s network rather than traditional phone lines.
- Routing Calls: The ITSP acts as a bridge between your business phone system and the public switched telephone network (PSTN), facilitating both inbound and outbound calls. This ensures that calls can be made to and received from any phone number globally.
- Internet-Based Communication: By leveraging the internet, the ITSP can route calls more efficiently and cost-effectively, providing seamless communication across various locations.
This connection to the ITSP is foundational to trunking, enabling businesses to utilize internet-based communication for their voice calls.
Digital Data Packets
Once the connection to the ITSP is established, voice calls are converted into digital data packets. This process involves several key steps:
- Voice Conversion: When a voice call is initiated, the analog voice signal is converted into digital data. This conversion is essential for transmitting the voice signal over the internet.
- Packetization: The digital voice data is then divided into small packets. Each packet contains a portion of the voice data along with necessary header information for routing.
- Transmission Over the Internet: These packets are transmitted over the internet to their destination. The use of packet-switched networks allows for efficient utilization of bandwidth and reduces the need for dedicated voice channels.
By converting voice calls into digital data packets, SIP trunking ensures that communication is both efficient and high-quality.
SIP-Compatible Systems
For SIP trunking to function effectively, businesses need to use SIP-compatible systems. These systems include:
- SIP-Compatible PBX Systems: A SIP-compatible PBX system is crucial for managing call routing and features. It handles the initiation, management, and termination of voice calls over the SIP trunks.
- VoIP Phones: VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) phones are designed to work with SIP trunking. They connect directly to the internet and use SIP to manage call signaling and media transfer.
- Adapters: For businesses that still use traditional analog phones, adapters can convert the analog signals into digital data, making them compatible with SIP trunking.
These SIP-compatible systems ensure seamless integration and communication, allowing businesses to fully leverage the benefits of SIP trunking.
Simplifying Communication
One of the significant advantages of SIP trunking is its ability to simplify communication by integrating various forms of communication into a single platform:
- Unified Communication: SIP trunking supports not just voice, but also video calls, messaging, and conferencing. This unification simplifies the communication infrastructure, reducing the need for separate systems for different communication forms.
- Enhanced Collaboration: By integrating multiple communication channels, SIP trunking enhances collaboration within the business. Employees can easily switch between voice, video, and messaging, improving productivity and efficiency.
- Scalability and Flexibility: SIP trunking allows businesses to scale their communication systems as needed. Adding new lines or features is straightforward, enabling quick adaptation to changing business requirements.
This integration and simplification of communication make SIP trunking a valuable asset for modern businesses.
Benefits of Digital Communication
Transitioning to digital communication through SIP trunking offers several benefits:
- Cost Savings: Digital communication reduces the need for traditional phone lines and associated costs. Businesses can save significantly on long-distance and international call charges.
- Improved Call Quality: With advancements in internet speed and quality, SIP trunking provides superior call quality compared to traditional phone lines.
- Reliability and Redundancy: SIP trunking offers higher reliability and redundancy. In case of a failure, calls can be rerouted to other locations or devices, ensuring business continuity.
By embracing digital communication, businesses can enhance their communication capabilities while reducing costs and improving reliability.
Integration with Existing Systems
SIP trunking can be seamlessly integrated with existing communication systems, offering flexibility and ease of transition:
- Compatibility with Legacy Systems: For businesses with existing legacy systems, SIP trunking can work alongside traditional phone systems. Adapters and gateways facilitate this integration.
- Phased Transition: Businesses can adopt SIP trunking in phases, gradually transitioning from traditional systems to full SIP deployment. This approach minimizes disruption and allows for smooth adaptation.
- Customization and Control: SIP trunking solutions offer high levels of customization and control. Businesses can tailor their communication systems to meet specific needs and preferences.
This seamless integration ensures that businesses can transition to SIP trunking without significant disruptions.
By understanding how SIP trunking works and its benefits, businesses can make informed decisions to enhance their communication systems. For more details on SIP trunking and its advantages, visit this comprehensive guide.
SIP trunking represents the future of business communication, offering a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution that can transform how businesses connect and collaborate.
Transitioning to SIP Trunking
Switching to SIP trunking requires certain key components:
- Reliable Internet Connection: A strong and stable internet connection is essential for SIP trunking to function efficiently.
- SIP-Compatible PBX System: Businesses need a PBX system that supports trunking to handle call routing and management.
- VoIP Phones or Adapters: VoIP phones or adapters are necessary to convert voice signals into digital data packets.
- Network Connection for Phones: Proper network infrastructure is needed to connect phones and ensure smooth communication.
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) numbers are also important in trunking as they allow businesses to assign individual phone numbers to users, facilitating direct calls without operator assistance.
Benefits of SIP Trunking
Cost Savings and Efficiency
- Reduced Costs: SIP trunking significantly reduces costs compared to traditional phone lines. Businesses can save on long-distance and international call charges.
- Simplified Pricing Models: With predictable monthly expenses, trunking offers a straightforward and budget-friendly pricing model.
Virtual Presence
- Centralized Communication: SIP trunking enables centralized communication across multiple devices and applications, enhancing productivity.
- Flexible Call Routing: Calls and messages can be easily routed to different devices, ensuring constant connectivity.
Space for Growth and Scalability
- Easy Scalability: SIP trunking allows businesses to scale their phone systems without the need for new infrastructure. Phone lines can be added on demand.
- Future-Proofing: As businesses grow, SIP trunking can accommodate increasing communication needs.
Reliable Technology
- Higher Reliability: SIP trunking offers higher reliability compared to traditional telephony services, with resilience in case of failures or disasters.
- Disaster Recovery: In the event of an outage, calls can be rerouted to other locations or devices, ensuring business continuity.
Drawbacks of SIP Trunking
Dependence on Internet Connectivity
- Internet Reliance: SIP trunking depends on a reliable internet connection. To mitigate this, businesses can implement redundant internet connections or backup cellular data.
Quality of Service (QoS) Issues
- Service Quality: QoS issues can arise due to bandwidth limitations. Implementing QoS prioritization policies or using a dedicated internet connection can help maintain call quality.
Security Vulnerabilities
- Security Risks: SIP trunking can be vulnerable to cyber threats. Using encrypted SIP trunks and enabling security features can enhance protection.
Power Dependency
- Power Outages: SIP trunking systems rely on power, making them susceptible to outages. Backup power systems or emergency analog lines can provide a solution.
SIP Trunking vs. PRI and VoIP
SIP trunking, PRI (Primary Rate Interface), and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) each have distinct characteristics:
- Technology: Trunking and VoIP use internet-based technology, while PRI relies on traditional phone lines.
- Scalability: Trunking and VoIP offer better scalability compared to PRI.
- Cost: Trunking and VoIP generally have lower costs than PRI.
- Mobility: Trunking and VoIP provide greater mobility, allowing users to access phone systems from various locations.
Trunking and VoIP offer advanced features and flexibility, making them more suitable for modern business needs compared to PRI.
Who Can Benefit from SIP Trunking?
Trunking is particularly beneficial for:
- Businesses with High Call Volume: Companies that handle a large number of calls can reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Businesses Needing Scalability: Organizations that require flexibility to scale their phone systems as they grow.
- Businesses Seeking Advanced Features: Companies looking for features like call routing, video conferencing, and unified communications.
Getting Started with SIP Trunking
Assessing Your Needs
Before transitioning to SIP trunking, it’s crucial to evaluate your business’s communication requirements. Start by assessing the current state of your phone system, including the number of lines, call volume, and the types of communication channels you use (voice, video, messaging). Identify any pain points or limitations in your current setup that you aim to address with SIP trunking. Consider your future growth plans and how SIP trunking can accommodate these changes. Understanding your needs will help you choose the right trunking solution and ensure a smooth transition.
- Current System Analysis: Review the existing phone infrastructure and determine the number of lines, usage patterns, and call volume.
- Identify Pain Points: Pinpoint issues such as high costs, limited scalability, or poor call quality.
- Future Requirements: Anticipate future communication needs, including potential expansions and increased call volumes.
- Integration Needs: Assess the need for integrating other communication channels like video conferencing and messaging.
Choosing a SIP Provider
Selecting the right trunking provider is a critical step in the transition process. Look for a provider with a proven track record of reliability and excellent customer support. Compare different providers based on their service offerings, pricing models, and customer reviews. Ensure the provider offers essential features such as QoS (Quality of Service) guarantees, robust security measures, and scalability options.
- Provider Reliability: Research the reliability and uptime guarantees of potential providers.
- Service Features: Compare features such as call routing, disaster recovery, and support for multiple communication channels.
- Pricing Models: Evaluate the pricing structure, including any hidden fees, to ensure cost-effectiveness.
- Customer Support: Ensure the provider offers 24/7 support and has a reputation for excellent customer service.
Preparing Your Network
A reliable and high-performing network is essential for SIP trunking. Conduct a thorough assessment of your current network infrastructure to ensure it can handle the increased data traffic from SIP trunking. Check your internet bandwidth to ensure it meets the requirements for high-quality voice and video calls. Implement Quality of Service (QoS) policies to prioritize voice traffic and minimize latency and jitter. Upgrade any outdated network hardware that could hinder performance.
- Bandwidth Assessment: Measure your current internet bandwidth and upgrade if necessary to support high-quality calls.
- QoS Implementation: Configure QoS settings to prioritize voice traffic over other types of data.
- Network Hardware: Upgrade routers, switches, and other network hardware to ensure they can handle SIP traffic efficiently.
- Security Measures: Implement firewalls and encryption protocols to protect against potential security threats.
Porting Your Numbers
If you wish to retain your existing phone numbers, you’ll need to port them to the new SIP system. Contact your current phone service provider to initiate the porting process. Ensure that your new SIP provider supports number porting and can handle the transition smoothly. Be aware of any potential downtime during the porting process and plan accordingly to minimize disruptions to your business operations.
- Contact Current Provider: Initiate the porting process by informing your current phone service provider.
- Coordinate with SIP Provider: Ensure the new SIP provider can support number porting and coordinate the transition.
- Downtime Planning: Plan for any potential downtime during the porting process to minimize business disruption.
- Verify Successful Porting: Test the ported numbers to ensure they work correctly with the new SIP system.
Configuring Your System
Once your network is prepared and your numbers are ported, it’s time to set up your SIP-compatible PBX system, VoIP phones, and adapters. Follow the SIP provider’s guidelines for configuring your equipment. Ensure that your PBX system is set up to handle SIP trunking and that all VoIP phones and adapters are correctly configured. Test the system thoroughly to identify and resolve any issues before going live.
- PBX Setup: Configure your PBX system to support trunking according to the provider’s guidelines.
- VoIP Phone Configuration: Set up VoIP phones and ensure they are correctly connected to the network and configured for SIP trunking.
- Adapter Setup: For legacy equipment, configure adapters to convert traditional voice signals to digital data packets.
- System Testing: Conduct extensive testing to identify and resolve any issues before fully deploying the system.
Training Your Staff
The final step in transitioning to SIP trunking is to train your staff on the new system. Provide comprehensive training on how to use the new SIP-compatible phones and any additional features. Ensure that employees understand how to handle common issues and whom to contact for support. Ongoing training sessions can help keep staff updated on new features and best practices, ensuring smooth and efficient communication.
- Initial Training: Conduct training sessions to introduce staff to the new system and its features.
- Troubleshooting Guidance: Provide instructions on how to troubleshoot common issues and whom to contact for support.
- Ongoing Training: Schedule regular training sessions to update staff on new features and best practices.
- User Manuals and Resources: Distribute user manuals and online resources to help staff become proficient with the new system.
Conclusion
SIP trunking offers a powerful solution for modern business communication, providing cost savings, scalability, and reliability. By understanding its benefits and requirements, businesses can enhance their communication efficiency and reduce expenses.