Have you ever wondered why businesses are moving away from traditional landline phones? The rise of internet-based communications has led to a significant shift from conventional telephone systems to IP telephony. Unlike traditional landlines that rely on dedicated circuits, IP telephony uses the internet to transmit voice, video, and data. This transformation is not just a trend but a revolution that is reshaping how companies communicate.
The global IP phone market has seen substantial growth, with businesses worldwide embracing this technology for its cost-effectiveness and flexibility.
This blogs explores IP telephony, how it works, and its benefits. Whether you’re new to the concept or looking to upgrade your current communication system, understanding IP telephony can help your business thrive in today’s digital age.
Read More: VoIP Callers: What are they and how do they work?
What Is IP Telephony?
IP telephony, or Internet Protocol Telephony, refers to a technology that allows voice, video, and data communications over the internet. Unlike traditional phone systems that use circuit-switched networks, IP telephony utilizes packet-switched networks, making it more efficient and cost-effective.
The primary difference between IP telephony and traditional telephone systems lies in the method of transmission. Traditional systems rely on physical lines and switches to connect calls, while IP telephony uses the internet to send and receive data packets. This shift from hardware-based to software-based systems has paved the way for more versatile communication methods.
Since its inception, IP telephony has evolved significantly. It began with simple VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) services that allowed basic voice calls over the internet. Today, it encompasses a wide range of communication tools, including video calling, conferencing, instant messaging, and even faxing. Businesses can now enjoy a unified communication experience that integrates seamlessly with other digital tools.
IP telephony is not just about making phone calls; it’s about enhancing communication capabilities. Video calls, for instance, enable face-to-face meetings without the need for travel. Conferencing allows multiple users to connect from different locations, fostering collaboration. Messaging and faxing over IP provide additional flexibility and convenience, making IP telephony a comprehensive solution for modern businesses.
How Does IP Telephony Work?
Understanding the inner workings of IP telephony involves grasping how data is transmitted over the internet. Unlike traditional phone systems that rely on dedicated circuits to connect calls, IP telephony converts voice signals into digital data packets. These packets are then transmitted over the internet to the recipient, where they are reassembled into audible sound. This process allows for more efficient use of resources and provides a foundation for various advanced communication features.
Conversion of Voice Signals into Digital Data Packets
The first step in IP telephony involves converting analog voice signals into digital data packets. This process starts with a device like a softphone or an IP phone capturing the sound of a voice and converting it into digital format. The conversion is achieved using a codec (coder-decoder), which compresses the voice data to reduce bandwidth usage while maintaining call quality. Once the voice is digitized, it is broken down into small packets of data, each containing a portion of the conversation.
These data packets are then assigned headers that include essential information such as the sender’s and recipient’s IP addresses, the packet’s sequence, and the type of data being transmitted. This information ensures that packets reach the correct destination and are reassembled in the proper order upon arrival, allowing for a smooth and coherent conversation.
Transmission of Data Packets Over the Internet
Once the voice signals are converted into digital data packets, they are transmitted over the internet. Unlike traditional phone systems that use a dedicated path for each call, IP telephony sends packets across the most efficient route available. This method is known as packet switching and allows multiple conversations to share the same network resources, making it more efficient than circuit-switched networks.
The internet, however, does not guarantee the order in which packets arrive at their destination. This is where protocols like the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) and the Real-time Control Protocol (RTCP) come into play. RTP is responsible for delivering the data packets in the correct sequence and ensuring that they arrive on time. RTCP works alongside RTP to provide feedback on the quality of the transmission, allowing adjustments to be made if needed to maintain call quality.
Key Protocols Involved in IP Telephony
Several key protocols play a crucial role in the operation of IP telephony. The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is one of the most important, as it establishes, manages, and terminates voice and video calls. SIP works by sending request and response messages between devices to set up a call, negotiate call parameters, and close the connection when the call is finished.
Another essential protocol is the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP), which is responsible for the actual transmission of data packets. RTP ensures that voice data is delivered in real-time, making sure that packets arrive in the correct order and without significant delay. The Real-time Control Protocol (RTCP) works alongside RTP to monitor transmission quality and provide feedback, allowing the system to make necessary adjustments to maintain call quality.
Additionally, the H.323 protocol is used in some IP telephony systems, particularly for multimedia communications. Although it is less common today due to the widespread adoption of SIP, H.323 provides a comprehensive framework for voice, video, and data communication over IP networks, making it a versatile option for certain applications.
Deployment Methods: IP PBX Systems and Hosted VoIP Solutions
IP telephony can be deployed in various ways, depending on the needs and preferences of the business. Two primary methods are IP PBX systems and hosted VoIP solutions.
An IP PBX (Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange) is a hardware or software-based phone system within a business that manages calls internally and externally. It connects internal users within the organization and manages their access to external networks. An IP PBX can handle many simultaneous calls, provide advanced features like call routing and voicemail, and integrate with other business applications.
On the other hand, hosted VoIP solutions involve outsourcing call management and routing functions to a service provider, which hosts the system in the cloud. This approach eliminates the need for businesses to maintain on-premises equipment, reducing costs and complexity. Hosted VoIP solutions are scalable and offer a wide range of features, making them an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
VoIP System Workflow: From Call Initiation to Delivery
The workflow of a VoIP system includes several critical steps that ensure smooth and efficient communication. When a user initiates a call, the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) sets up the connection between the caller and recipient. This process involves sending a SIP request to the recipient’s device, which responds with a confirmation if it is available to take the call.
Once the connection is established, SIP trunking provides the pathway for the call to travel over the internet, bypassing traditional telephone lines. SIP trunking allows voice data to be transmitted as packets, reducing costs and increasing flexibility. The call data is then managed and processed in the cloud, where it undergoes various quality control measures to ensure a clear and reliable connection.
Finally, the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) handles the delivery of the voice data, ensuring that it arrives at the recipient’s device in the correct order and without significant delay. The Real-time Control Protocol (RTCP) monitors the quality of the transmission and provides feedback, allowing the system to make adjustments if needed. This comprehensive workflow enables VoIP systems to provide high-quality voice communication over the internet, making IP telephony a viable alternative to traditional phone systems.
Advantages of IP Telephony’s Internet-Based Workflow
- Efficiency: By using packet switching, IP telephony maximizes the efficiency of network resources, allowing multiple calls to share the same bandwidth without compromising quality.
- Flexibility: The use of internet-based protocols allows for a wide range of communication features, including voice, video, and data, all within a single platform.
- Scalability: Businesses can easily scale their communication systems up or down based on their needs, without the need for extensive hardware investments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By bypassing traditional telephone lines and using the internet for communication, businesses can reduce their costs significantly, especially for long-distance and international calls.
IP Telephony vs. VoIP: Understanding the Differences
The terms IP telephony and VoIP are often used interchangeably, but they are not entirely synonymous. IP telephony is a broad term encompassing all internet-based communications, including voice, video, and data. VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, is a subset of IP telephony that specifically refers to transmitting voice communications over the internet.
While both IP telephony and VoIP rely on the same underlying technology, their scopes differ. VoIP is focused on voice calls, whereas IP telephony includes a wider range of services, such as video conferencing, messaging, and data sharing. In essence, all VoIP services are a part of IP telephony, but not all IP telephony services are VoIP.
In the telecommunications industry, these terms are often used interchangeably due to their similarities. However, understanding the distinction is essential for businesses looking to implement the right solution for their communication needs. By recognizing the differences, companies can choose a system that best aligns with their requirements, whether focusing on voice communications or integrating multiple channels.
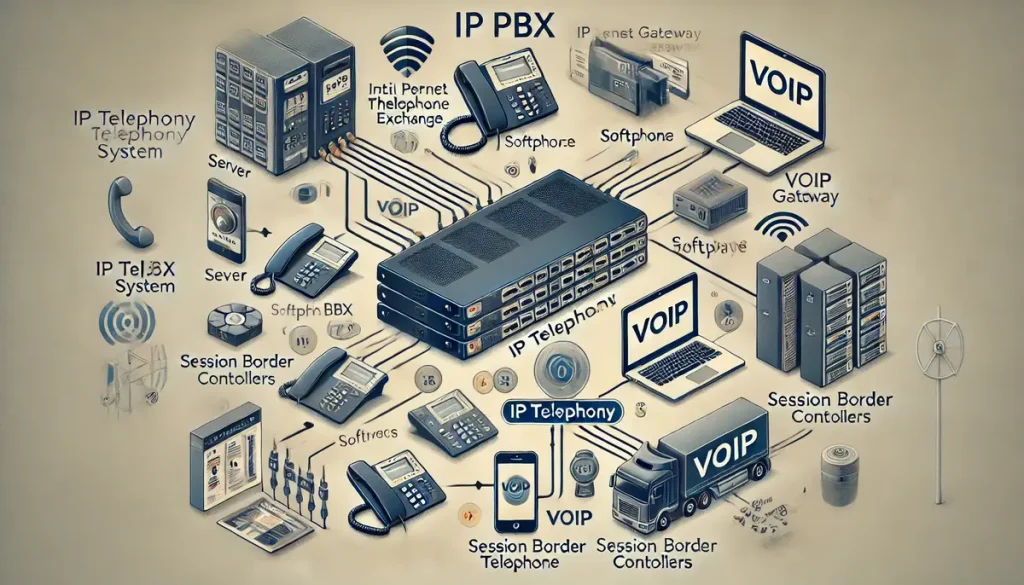
Key Components of IP Telephony Systems
An IP telephony system is built on several crucial components that work together to facilitate efficient and reliable communication. Each element plays a distinct role in ensuring that voice, video, and data transmissions are managed effectively over the internet. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the key components that make up an IP telephony system:
IP PBX: The Central Hub of Communication
The IP PBX (Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange) is the central hub of an IP telephony system. It is responsible for managing and routing all internal and external calls within an organization. Unlike traditional PBX systems, which rely on analog lines and switches, an IP PBX uses the internet to transmit voice data, making it a more versatile and scalable solution.
- Call Management and Routing: The primary function of an IP PBX is to handle call management and routing. It connects users within the organization and directs their calls to the appropriate internal or external lines. This allows for efficient communication and resource allocation, ensuring that all calls are handled promptly and correctly.
- Flexibility and Scalability: One of the key advantages of an IP PBX is its flexibility and scalability. Since it operates over the internet, adding new users or expanding the system requires minimal effort. Businesses can easily scale their communication systems to meet changing needs without investing heavily in new hardware or infrastructure.
- Integration with Other Systems: IP PBX systems can integrate seamlessly with other business applications, such as customer relationship management (CRM) software and email platforms. This integration allows for unified communications, where voice, video, and data are combined into a single, cohesive system, enhancing productivity and collaboration.
- Advanced Features: In addition to basic call management, IP PBX systems offer a range of advanced features that improve communication efficiency. These include voicemail to email, call forwarding, call recording, and automated attendants. These features are typically managed through a user-friendly web interface, making them accessible to all users.
Softphones: The Modern Alternative to Traditional Phones
Softphones are software-based alternatives to traditional hardware phones, allowing users to make and receive calls through their computers, tablets, or mobile devices. They provide the same functionality as physical phones but with added flexibility and convenience.
- Software-Based Communication: Softphones are applications installed on a device that uses the internet to handle voice and video calls. They eliminate the need for physical phones, reducing costs and simplifying communication setups. Users can access their softphone from anywhere with an internet connection, making it an ideal solution for remote or mobile workers.
- Integration with Business Applications: Softphones often integrate with other software applications, such as CRM tools and email clients. This integration allows for seamless communication and data sharing, enhancing workflow efficiency and productivity. For example, users can make calls directly from their CRM or email interface, streamlining their daily tasks.
- Enhanced Features and Flexibility: Softphones offer a range of features that are not available on traditional phones. These include video conferencing, instant messaging, and presence indicators, which show the availability of other users. Additionally, softphones can be customized with various plugins and add-ons, allowing users to tailor the application to their specific needs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Since softphones do not require physical hardware, they are a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes. They reduce the need for maintenance and upgrades associated with traditional phone systems, allowing companies to allocate resources more efficiently.
VoIP Gateways: Bridging IP Telephony with Traditional Phone Systems
VoIP gateways are crucial components in IP telephony systems that enable seamless communication between different types of phone systems. They act as bridges, converting analog signals from traditional phones into digital data for transmission over the internet and vice versa.
- Analog to Digital Conversion: The primary function of a VoIP gateway is to convert analog signals from traditional telephones into digital data that can be transmitted over IP networks. This conversion allows businesses to maintain their existing phone infrastructure while transitioning to IP telephony.
- Connecting to the PSTN: VoIP gateways connect IP telephony systems to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), enabling communication between IP-based and traditional phone systems. This connectivity ensures that businesses can communicate with clients and partners who still use conventional phone services.
- Seamless Integration: VoIP gateways facilitate seamless integration between IP telephony and existing telephony systems, allowing businesses to leverage their current investments while adopting new technology. This integration helps minimize disruption during the transition to IP telephony and ensures compatibility with various devices and networks.
- Support for Multiple Interfaces: VoIP gateways support multiple interfaces, including analog, digital, and IP, making them versatile and adaptable to various communication environments. They can handle a range of protocols and codecs, ensuring that voice quality is maintained across different networks and devices.
Session Border Controllers (SBCs): Ensuring Security and Quality
Session Border Controllers (SBCs) are essential for maintaining network security and managing communication quality in IP telephony systems. They act as gatekeepers, controlling the flow of data packets between different networks and ensuring that all communications are secure and efficient.
- Network Security: One of the primary functions of an SBC is to protect the IP telephony network from security threats, such as denial-of-service attacks and eavesdropping. SBCs monitor and control the flow of data packets, ensuring that only authorized traffic is allowed through. They also encrypt voice data, preventing unauthorized access and maintaining privacy.
- Managing Call Quality: SBCs play a vital role in managing call quality by prioritizing voice traffic over other types of data. This prioritization, known as Quality of Service (QoS), ensures that voice calls receive the necessary bandwidth and resources to maintain high-quality communication. SBCs also monitor network conditions and adjust call parameters to minimize latency, jitter, and packet loss.
- Regulatory Compliance: In addition to security and quality management, SBCs help ensure that IP telephony systems comply with various regulatory requirements. They can enforce policies related to data retention, call recording, and emergency services, helping businesses meet their legal obligations.
- Interoperability: SBCs facilitate interoperability between different IP telephony systems, ensuring that devices and networks can communicate effectively. They handle protocol translation and media transcoding, allowing for seamless communication between different platforms and devices.
Network Infrastructure: The Backbone of IP Telephony
A robust network infrastructure is essential for supporting IP telephony systems. It includes high-speed internet connections, adequate bandwidth, and reliable networking equipment, all of which are necessary for ensuring that IP telephony services operate efficiently without disruptions or quality issues.
- High-Speed Internet: A high-speed internet connection is critical for IP telephony, as it provides the necessary bandwidth for transmitting voice, video, and data packets. Without sufficient internet speed, calls may experience latency, jitter, or packet loss, resulting in poor call quality and communication issues.
- Adequate Bandwidth: Adequate bandwidth is essential for supporting multiple simultaneous calls and other data-intensive activities. Businesses must ensure that their network can handle the increased traffic associated with IP telephony, especially if they have a large number of users or use additional services like video conferencing.
- Reliable Networking Equipment: Reliable networking equipment, such as routers, switches, and firewalls, is crucial for maintaining a stable and secure IP telephony system. These devices manage the flow of data packets, prioritize voice traffic, and protect against security threats, ensuring that communications are consistent and uninterrupted.
- Network Redundancy and Resilience: To minimize downtime and ensure continuous communication, businesses should implement network redundancy and resilience measures. This includes having backup internet connections, redundant hardware, and failover systems that can take over in case of a primary network failure. By building a resilient network infrastructure, businesses can provide a reliable and high-quality IP telephony experience for their users.
Benefits of IP Telephony for Businesses
IP telephony offers numerous advantages for businesses, making it an attractive alternative to traditional phone systems. Here are some key benefits:
- Reduced Costs: One of the most significant benefits of IP telephony is cost savings. Unlike traditional business phone plans that require expensive infrastructure and maintenance, IP telephony operates over the internet, reducing the need for costly hardware and long-distance charges. Businesses can save significantly on their communication expenses, especially those with international clients or remote teams.
- Advanced Features Without Extra Hardware: IP telephony provides access to advanced features that would typically require additional hardware in traditional systems. These include call routing, recording, video conferencing, and voicemail to email, all of which can be managed through a simple software interface. Businesses can enhance their communication capabilities without investing in new equipment.
- Increased Accessibility: With IP telephony, users can make and receive calls from anywhere with an internet connection. This increased accessibility is ideal for businesses with remote or mobile workers, ensuring that employees can stay connected regardless of location. It also enables companies to expand their operations globally without needing physical offices in every region.
- Unified Communications: IP telephony integrates seamlessly with other business tools, such as CRM systems, email, and collaboration platforms, creating a unified communications environment. This integration streamlines operations, improves productivity, and enhances customer service by providing a cohesive communication experience across all channels.
Challenges With IP Telephony and How to Overcome Them
While IP telephony offers many benefits, it also presents some challenges that businesses must address. Here are the main issues and tips for overcoming them:
- Quality of Service (QoS): Quality of Service (QoS) can be a concern with IP telephony, as issues like network jitter and latency can affect call quality. To mitigate these problems, businesses should ensure they have a robust network infrastructure and prioritize VoIP traffic. Implementing QoS policies can help maintain call quality by managing bandwidth allocation and reducing latency.
- Security Concerns: Security is another critical consideration with IP telephony. VoIP calls can be intercepted or eavesdropped on if not properly secured. Using encryption protocols, firewalls, and SBCs can help protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access. Choosing a VoIP service provider with robust security measures is also essential.
- Compatibility Issues: Integrating IP telephony with existing telephone devices can sometimes pose compatibility challenges. Businesses should opt for VoIP systems that support a wide range of devices and protocols to ensure seamless integration. Regularly updating software and firmware can also help address compatibility issues.
- Reliability: IP telephony relies on internet connectivity, making it susceptible to outages and disruptions. To minimize downtime, businesses should choose a reliable VoIP service provider with redundant network infrastructure and offer a robust service level agreement (SLA). Having a backup internet connection or failover system can also ensure continuity in case of an outage.
Conclusion
IP telephony represents a significant advancement in business communications, offering numerous benefits such as reduced costs, advanced features, and increased accessibility. However, it also presents challenges that businesses must address to maximize its potential. By understanding IP telephony and implementing strategies to overcome its challenges, companies can enhance their communication capabilities and stay competitive in today’s digital landscape.
As technology continues to evolve, IP telephony is set to play an increasingly important role in modern business communications. Businesses that adopt this technology can expect to benefit from its cost-efficiency, scalability, and advanced features, positioning them for success in the future.