How crucial is data governance in today’s data-driven world? As organizations increasingly rely on data to drive decisions and strategies, ensuring proper data management and ownership becomes essential. Did you know that according to Gartner, poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually? This staggering statistic underscores the importance of effective data governance.
How can businesses ensure their data assets are accurately managed and regulatory compliant? This blog explores the intricate relationship between data ownership and data governance, highlighting its importance in maximizing the value of data assets, ensuring data accuracy, and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Read More: AI Data Governance: 7 Key Consumer Rights
Introduction to Data Governance and Data Ownership
Data governance refers to the framework of policies, procedures, and standards that ensure the effective and efficient use of data within an organization. The primary purpose of data governance is to maximize the lifecycle value of data assets, ensuring they are accurate, reliable, and consistent.
- Maximizing data asset lifecycle value: Effective data governance ensures that data is properly managed throughout its lifecycle, from creation to disposal.
- Ensuring data accuracy, reliability, and consistency: By implementing robust governance practices, organizations can maintain high-quality data that supports decision-making processes.
Importance of Data Governance in Organizations
Data governance is crucial for several reasons, including regulatory compliance, risk mitigation, and enhancing data quality.
- Regulatory compliance: Adhering to data governance policies helps organizations comply with various regulations and standards, reducing the risk of legal penalties.
- Mitigating risks of data breaches: Effective data governance minimizes the risk of data breaches by implementing stringent security measures and protocols.
Why is Data Ownership Important in Data Governance?
Ensuring Data Accuracy, Reliability, and Security
Data ownership ensures that data is managed with the highest standards of accuracy, reliability, and security.
- Controlled access to data: Data owners establish and enforce access controls to ensure only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
- Accountability and Responsibility: Clear accountability ensures data is used appropriately and in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Challenges Without Data Ownership
Without defined data ownership, organizations may face significant challenges, including data quality issues, security breaches, and compliance violations.
- Data quality issues: Lack of ownership can lead to inconsistent and inaccurate data.
- Security breaches: Inadequate data management can increase the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Compliance violations: Failure to comply with regulatory requirements can result in legal and financial penalties.
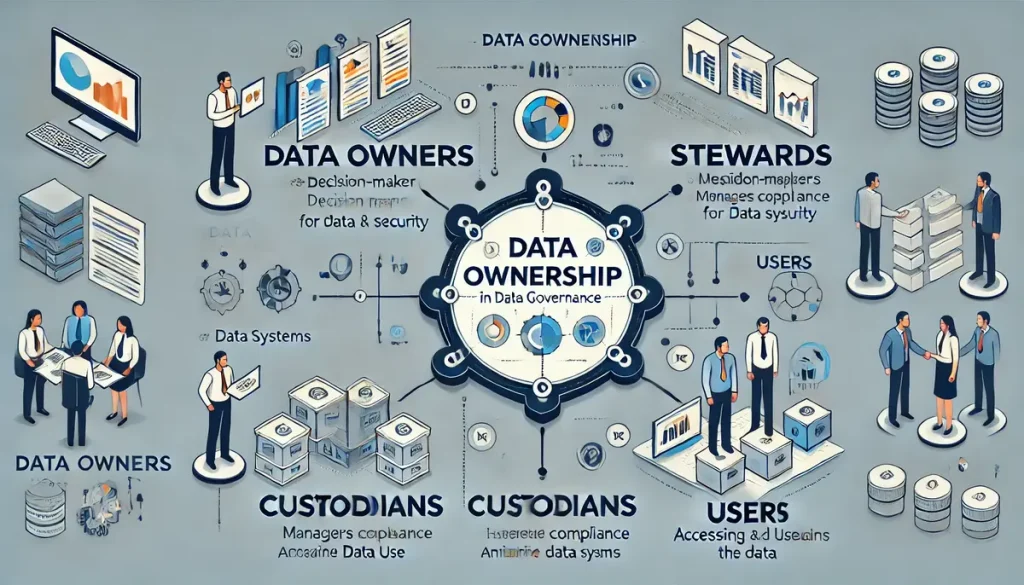
Data Ownership Model – Understanding the Framework
A robust data ownership model is essential for effective data governance. This model delineates the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders, ensuring that data is managed efficiently and securely. Key elements of the data ownership model include:
Data Owners
Data owners are individuals who are accountable for the data within their domain. They have the ultimate authority and responsibility for ensuring that the data is properly managed, maintained, and utilized. Their responsibilities include:
- Defining data policies: Data owners establish policies related to data quality, security, and access to ensure consistency and compliance.
- Ensuring data accuracy and reliability: They oversee the processes that maintain the integrity and reliability of the data.
- Managing data security: Data owners are responsible for implementing security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and breaches.
Data Stewards
Data stewards manage data on behalf of the data owners. They are responsible for the day-to-day management of data, ensuring it meets the established standards and policies. Their roles include:
- Data quality management: Data stewards monitor and maintain the quality of data, ensuring it is accurate, complete, and consistent.
- Documentation: They document data processes, policies, and procedures to ensure transparency and traceability.
- Coordination: Data stewards coordinate with data owners, custodians, and users to resolve data issues and implement improvements.
Data Custodians
Data custodians are responsible for storing, managing, and protecting data. They handle the technical aspects of data management, ensuring the data is available and secure. Their duties include:
- Data storage: Custodians manage the storage infrastructure, ensuring data is stored securely and efficiently.
- Data protection: They implement and maintain security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Data backup and recovery: Data custodians ensure that data is regularly backed up and can be recovered in case of data loss or corruption.
Data Users
Data users are individuals who access and utilize data for their job functions. They must adhere to the policies and procedures set by data owners and stewards. Their responsibilities include:
- Accessing data appropriately: Data users must follow access policies and use data only for authorized purposes.
- Maintaining data integrity: They should ensure that their use of data does not compromise its accuracy or reliability.
- Reporting issues: Data users should report any data-related issues or inconsistencies to data stewards or owners.
Data Owner Responsibilities and Best Practices
Data owners play a crucial role in the data governance framework. They have several critical responsibilities that ensure data is managed effectively and securely. Best practices for data owners include:
Defining Data Policies
Data owners must establish comprehensive data policies to guide the management and use of data. These policies cover various aspects, including:
- Data quality policies: Define standards for data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Outline processes for data validation, cleansing, and maintenance.
- Data security policies: Include guidelines for protecting data from unauthorized access, breaches, and other security threats. Specify access controls and monitoring procedures.
- Data access policies: Define who can access data, under what conditions, and how access is granted and revoked. Ensure access policies align with the organization’s security and compliance requirements.
Data Quality Management
Ensuring data quality is a fundamental responsibility of data owners. They must establish and monitor quality standards to maintain accurate, complete, and consistent data. Key activities include:
- Defining data quality standards: Set clear criteria for data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Ensure these standards are communicated and understood across the organization.
- Monitoring data quality: Regularly audit and review data to identify and address quality issues. Implement data validation and cleansing processes to maintain high-quality data.
- Improving data quality: Work with data stewards and custodians to implement improvements and resolve data quality issues. Promote a culture of data quality within the organization.
Data Security Management
Data owners are responsible for protecting data from unauthorized access and breaches. This involves implementing robust security measures and monitoring data access. Best practices include:
- Defining access controls: Establish access controls based on the sensitivity and criticality of data. Ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
- Monitoring data access: Regularly review access logs and monitor data usage to detect and prevent unauthorized access. Implement automated tools and processes for continuous monitoring.
- Responding to security incidents: Develop and implement procedures for responding to data security incidents. Ensure incidents are promptly reported, investigated, and resolved.
Data Access Management
Effective data access management ensures that data is used appropriately and in compliance with organizational policies. Data owners must define and enforce access policies to regulate how data is accessed and used. Key practices include:
- Establishing access policies: Define who can access data, the conditions for access, and the procedures for granting and revoking access. Ensure these policies align with security and compliance requirements.
- Enforcing access policies: Implement mechanisms to enforce access policies, such as access controls and authentication processes. Regularly review and update access policies as needed.
- Monitoring data access: Continuously monitor data access to ensure compliance with policies and detect any unauthorized access. Use automated tools and processes for efficient monitoring.
Best Practices for Successful Data Ownership
Establishing a Data Governance Council
A data governance council oversees data governance policies and procedures, ensuring they are effectively implemented across the organization.
- Overseeing data governance policies and procedures: The council ensures that data governance policies are followed and updated as needed.
- Defining Data Standards: Establish clear standards for data quality, security, and access.
Defining Data Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly defining data roles and responsibilities ensures effective data management and accountability.
- Clear roles for data management: Define the responsibilities of data owners, stewards, custodians, and users.
- Communicating Data Governance Policies and Procedures: Ensure all stakeholders understand their roles and responsibilities in data governance.
Who Should be a Data Owner?
Recommendations for Data Ownership
Placing data ownership on the business side rather than the IT/data side ensures that data is managed across the organization and aligned with business objectives.
- Placing data ownership on the business side vs. IT/data side: This approach ensures that data ownership aligns with business goals and strategies.
- Ensuring data is managed across the organization: Data ownership should be distributed to ensure comprehensive data management.
Challenges and Potential Solutions in Implementing Data Ownership in Data Governance
Common Challenges
Implementing data ownership in data governance can present challenges such as a lack of understanding of responsibilities, resource constraints, and resistance to change.
- Lack of understanding of data owner responsibilities: Clear communication and training can help address this issue.
- Lack of resources for implementing data governance: Allocate sufficient resources to support data governance initiatives.
- Resistance to change from stakeholders: Engage stakeholders and demonstrate the benefits of data ownership.
Potential Solutions
Effective communication, training, and linking business value to data management are key strategies to overcome challenges in implementing data ownership.
- Effective communication and training: Provide comprehensive training to ensure stakeholders understand their responsibilities.
- Highlighting benefits for data owners and the organization: Demonstrate how effective data management benefits both data owners and the organization.
- Linking business value to data management: Show how data governance supports business objectives.
Conclusion
Data ownership is crucial for ensuring effective data management and governance, supporting organizational goals and compliance requirements. Implementing data ownership requires clear communication, training, and resource allocation to address potential challenges. Effective data ownership enhances data quality, security, and compliance, benefiting both organizations and individuals involved in data management.
Data ownership is a fundamental component of data governance that ensures data is managed with the highest standards of accuracy, reliability, and security. By implementing a robust data ownership model and addressing potential challenges, organizations can maximize the value of their data assets and support their strategic objectives.